In our fast-changing tech world, mobile apps have smoothly become part of our daily lives, driving innovation across industries. With the mobile app industry booming, meticulous mobile app testing is now more crucial than ever.
Mobile apps need to be tested on a variety of software and hardware platforms and under different network connectivity conditions. Meticulous app testing ensures a seamless user experience devoid of glitches, regardless of the device in use.
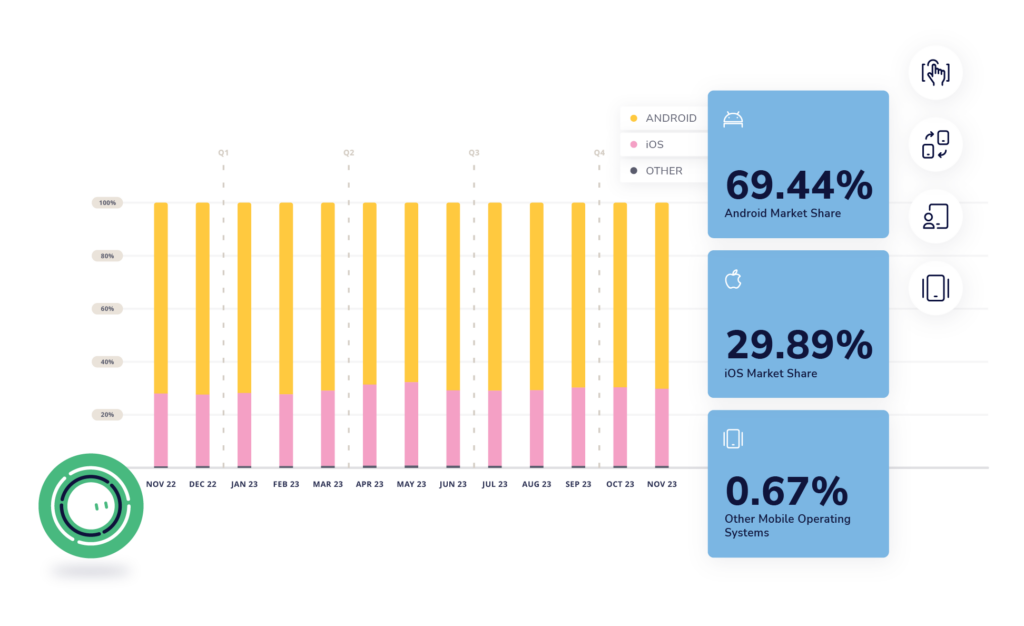
In the journey of app testing, adapting your app’s compatibility to the prevalent operating systems is key. Android and iOS lead the mobile OS domain, owning a combined 98% market share. However, these platforms differ extensively, bringing complexities to mobile app development and testing.
Let’s dive into some of the major differences between Android and iOS that impact mobile app testing.
Differences Between Android and iOS in Mobile App Testing
System Type: Open or Closed
Android, from Google, is open-source, using Linux OS. It’s known for adaptability and customization, letting developers tailor the OS to their needs. In contrast, iOS, Apple’s closed-source proprietary platform, limits access to its source code.
Android’s open-source platform makes it the favored OS among developers to perform advanced testing on mobile apps, as it’s more straightforward than iOS.
Device Types and the Number of Devices
Mobile app testing depends on the devices you target to test your app. Android’s challenge lies in a diverse list of devices from various manufacturers, differing in size, screen resolution, form factors, and hardware configurations.
iOS devices, all produced by Apple, provide an easier testing experience due to uniform screen resolutions and limited device types.
Software Updates
Android devices can use older software versions, so not all devices run on the same software version. Android testers must spend more time to deliver a consistent experience across all Android devices.
iOS devices receive software updates simultaneously and have fewer versions, simplifying app testing.
App Security
Old Android versions don’t receive newer security updates and built-in protection, so they are more vulnerable to hacking. Tools in the Google Play Store also allow users to access and change the source code of an app’s APK. Android app developers and testers must take extra steps to ensure their app code is secure and protected from malicious attacks.
iOS is renowned for its robust security features, and its closed-source platform makes it more challenging for hackers to perform malicious attacks on iOS devices. Thus, testers don’t have to spend as much time ensuring their app security is up to snuff.
App Availability
While the Google Play Store is more developer-friendly, its app approval process is far less strict than the Apple App Store. Developers must spend extra time ensuring there are no security loopholes in their app before publishing, since Google may not catch those issues before publishing their app.
Apple, on the other hand, has strict review guidelines for apps submitted to the Apple App Store. iOS testers must spend more time performing comprehensive tests to ensure their app passes Apple’s inspection.
Improving Your Mobile App Testing
Mobile app testing is a pivotal part of the app development process to ensure apps meet user expectations, function seamlessly, and provide exceptional user experiences. While both Android and iOS platforms demand rigorous testing, their differences pose distinct challenges to testers.
However, mobile app testing tools like Appium, Selenium, and Sofy have simplified and improved the app testing process. You can use these tools, which include cloud-based device labs, crash reports, and performance testing tools, to improve efficiency and productivity so you can spend more time creating better products, faster.